
It's time to talk about neutral wire color. While all wire colors are important to understand and utilize properly, the neutral wire is a consistently overlooked piece of any electrical system. Neutral wires have the important task of returning currents to the original power source; this is a necessary function of AC power, and we need to be able to identify these wires properly and make sure we use them for the right voltage connections.
Electricity is so omnipresent we often don't think about how it works. We can just flip a switch or plug in a cord and boom: we have light. We often don't think of it until either the power goes out or there's some kind of wiring malfunction.
In industrial facilities, where electricity takes part in nearly every aspect of what workers do, the importance of adhering to proper wiring protocols and wiring color codes is all the more crucial. The best way to stay up to code and accident-free electrically speaking is to adhere to wire color codes. But first, it's best to understand exactly what a neutral wire is, why it's important, and how to identify a neutral wire by color.
The Importance of Neutral Wire
There are many myths and misnomers about the neutral wire and what it does. It's commonly confused with ground wires. Some folks may not even know in what electricity systems these wires are found.
Neutral wires only exist in AC power; DC power consists of a positive, a negative, and a ground. AC power, on the other hand, have "hot" wires (which come in three phases), a neutral, and a ground. It's the neutral wire that allows for the current to alternate, since the neutral wire acts as the roadway back to power source.
The neutral wire is often confused with ground wire, but in reality, they serve two distinct purposes. Neutral wires carry currents back to power source to better control and regulate voltage. Its overall purpose is to serve as a path to return energy. Ground wires are electrical paths designed to carry fault currents when a power abnormality occurs. They don't carry currents-their purpose is to provide operator safety.
The best example of a ground wire doing its job is when lightning strikes a building, the ground wire will take all that excess energy and deliver it away from the house so that your TV or computer doesn't blow out.
Things to know about Neutral:
- Neutrals are NOT the same as ground wires
- Neutrals serve to carry currents back to power source
- The neutral is a crucial component in AC power
Why Are There Different Types of Neutral Wire Color?
AC Power comes in a variety of types based on the number of volts the wires carry. There are specific wire color codes for different volt classifications. These colors have to be different because the wires need to be composed according to the amount of voltage they'll be used for.
It's important to be able to identify and correctly use the appropriate wires for the right application to avoid electrical problems.
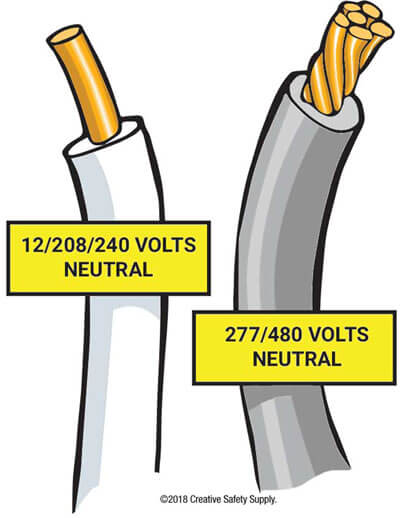
AC Power (12/208/240 volts)
AC power comes in a variety types based upon the number of volts the wires will be carrying. This voltage is often found in homes and businesses that don't require a lot of energy.
For AC Power using these amounts of voltage, the neutral wire color will be white.
AC Power (277/480 volts)
Common in manufacturing and industrial environments, these high-voltage connections abide by different wire colors. Since these connections have more serious potential for deadly electrocution or other critical injuries, it's crucial to get color codes correct.
For AC Power using these amounts of voltage, the neutral wire color will be gray.
Beware: Data Wiring
Unlike electrical wiring, Data wiring does not adhere to wire color code standards, but that doesn't mean that these wires shouldn't be handled with care. While it's true that data wires are used predominantly to transmit information rather than electricity, some of the networking cables will have enough active electricity within them to cause a hazard.
Certain devices-an IP phone, for example - use "power over Ethernet." This means it get its energy from the network cable to which it's connected. If these data wires get frayed or cut, they can cause fires or shock.
It's a good practice to label or attach warning signs near these cables to remind workers to use caution.
Since it's important that you have a good idea of the state of your facility's wiring, it might be worth it to pay extra close attention to your electrical system on your next Gemba walk.
Similar Articles
- Electrical Wiring (Wire Color Codes)
- Electrical Wire Colors
- Safety Colors (OSHA Guidelines and Color Codes)
- Selecting a Marker Size for Wire Marking
- Pipe Color Codes – ANSI/ASME A13.1
- ANSI Color Codes for Pipe Marking
- Cable Management
- Arc Flash [Facts, Safety Requirements & PPE]
- Heat Shrink Tubing
- ANSI TIA 606-B Cable Labeling Standards


