
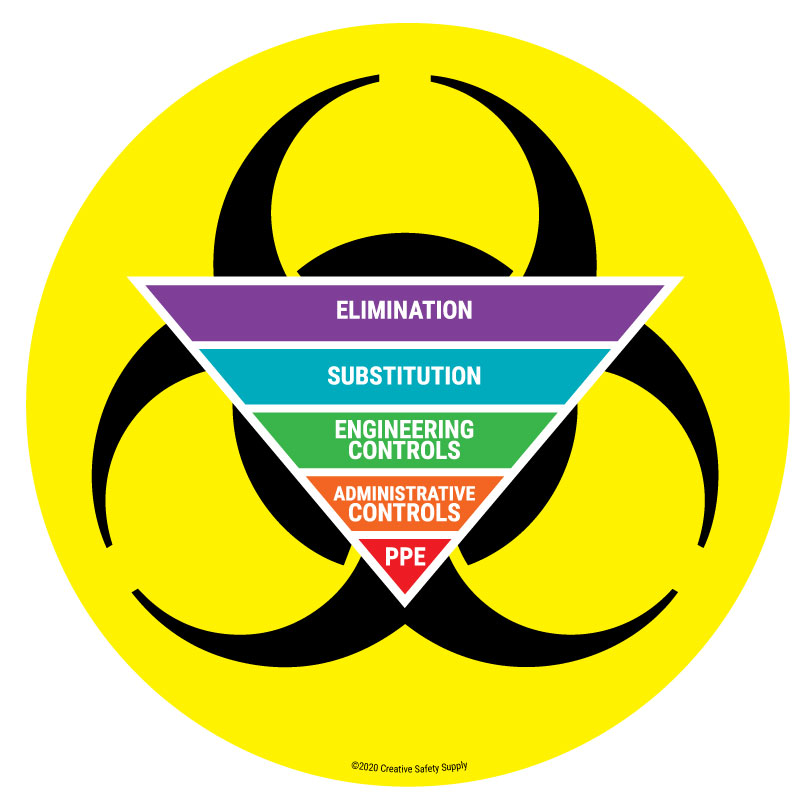
Biological hazards, also known as biohazards, refer to biological substances that pose a threat to the health of living organisms, primarily that of humans. Examples of biohazards include bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, toxins, and certain animal and plant products. Any material contaminated with these substances, such as blood, bodily fluids, or animal waste, is also considered a biohazard.
Biohazards can be found in a wide array of settings, including hospitals, laboratories, research facilities, food production, agriculture, and even everyday environments. They pose risks to human health and require careful handling and management.
Similar Glossary Terms
- Hierarchy of Controls
- Administrative Controls
- Industrial Hygiene
- Environmental Hazard
- Safety Engineering
- Health Hazard
- Pinch Points
- Indoor Air Quality (IAQ)
- Injury Prevention


