
An arc flash and an arc blast are both dangerous results of an electrical fault, but they differ in their manifestations. An arc flash is the light and heat generated when electricity jumps between conductors through the air, while an arc blast is the resulting pressure wave from the rapid expansion of air and vaporized material caused by the arc. That means the arc flash is the thermal and visual phenomenon, and the arc blast is the explosive force.
Arc Flash vs Arc Blast Hazards
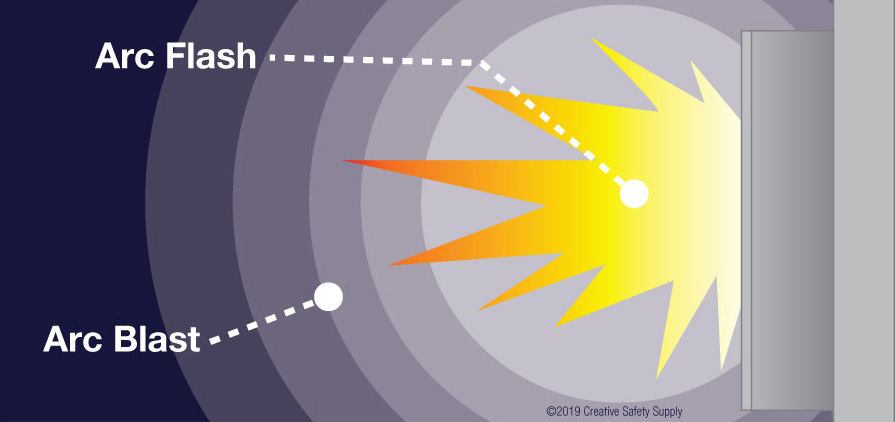
Both Arc flash and arc blast are serious hazards; however, they present distinct dangers. Arc flash can cause severe burns and potential blindness due to intense heat and light, while arc blast involves a pressure wave that can knock people down, causing injuries from falls and potentially leading to hearing damage.
It’s important to understand arc flash and arc blast and their dangers to take appropriate safety measures and have protective equipment when working with electricity.
Additional Arc Flash facts:
- According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), arc flash incidents are responsible for 80% of all electrical injuries in the U.S. every year. Source: https://www.nfpa.org/education-and-research/research/nfpa-research/fire-statistical-reports/firefighter-injuries-in-the-united-states?l=0
- The most common cause of arc flash is human error, such as using improper tools, dropping metal objects, or touching live parts. Source: https://www.eaton.com/us/en-us/company/news-insights/reset-safety-arc-flash/common-causes-of-arc-flash.html
- The duration of an arc flash can range from a fraction of a second to several seconds, depending on the fault current and the protective devices in the system. Source: https://www.conney.com/websphere/ResourcesTabs/Knowledge-Base/Whitepapers/ArcFlash_Whitepaper.pdf
- The sound level of an arc blast can exceed 160 decibels, which is louder than a jet engine or a gunshot. This can cause permanent hearing loss or rupture of the eardrums. Source: https://www.nfpa.org/News-and-Research/Data-research-and-tools/Electrical/Fatal-electrical-injuries-at-work
- The pressure wave of an arc blast can also damage the lungs, heart, and other internal organs. It can also cause concussions, fractures, and spinal injuries. Source: https://elecsafety.co.uk/what-is-arc-flash/
- The best way to prevent arc flash and arc blast injuries is to follow the NFPA 70E standard, which provides guidelines for electrical safety in the workplace. This includes de-energizing equipment before working on it, wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and maintaining a safe distance from energized parts. Source: https://www.nfpa.org/News-and-Research/Data-research-and-tools/Electrical/Fatal-electrical-injuries-at-work
Similar Questions
- What is an arc flash?
- Who is at risk of an arc flash?
- What is an arc flash boundary?
- What is an electrical arc?
- At what voltage can an arc flash occur?
- How does an arc flash occur?
- Where do arc flashes occur?
- How do I prevent an arc flash from happening?
- What causes electrical arcing?


