
A distribution board is a part of an electrical system that takes electricity from a main source and feeds it through one or more circuits to distribute the electricity throughout a facility. This is often called an electrical panel, panelboard, or even a fuse box. Virtually all homes and businesses will have at least one distribution board built in, which is located where the main electrical line enters the structure. The size of the board will depend on the amount of electricity coming in and how many different circuits need to be installed.
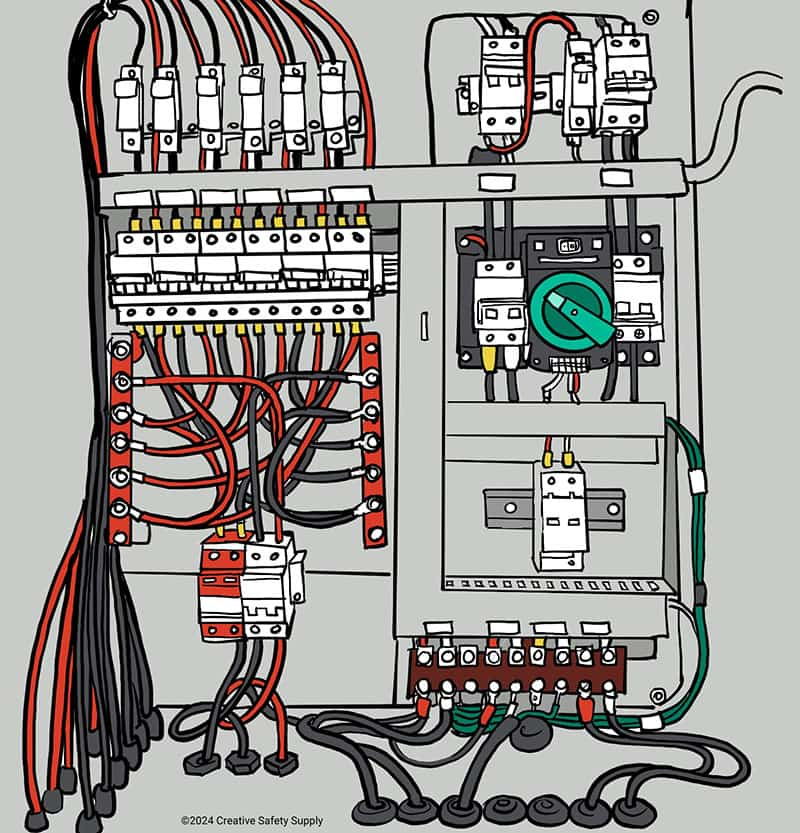
Distribution boards allow all your electrical equipment to operate safely throughout the entire area. You can, for example, install a small 15-amp circuit breaker into the distribution board to supply one area of the facility with the power it needs. This will only allow up to 15 amps of electricity to pass from the main electrical line into the area where it is used, which means that area can be serviced with smaller and less expensive wire. It will also prevent a surge (of greater than 15 amps) from entering equipment and potentially causing damage.
For areas that need more electricity, you would install circuit breakers that allow more electricity through. Having the ability to take one main circuit that provides 100 or more amps of power and distributing it throughout the facility based on how much power is needed in a given place is not only far safer than just having full access to the full amperage at all times, but it is also much more convenient. If, for example, there is a surge in one area, it will only trip the breaker on the distribution board for that one circuit. This prevents an electrical outage to other areas of the home or business
Additional Distribution Board facts:
- A distribution board is the main electrical supply system for any commercial or residential entity. The main cable comes into the distribution board and then via breakers get distributed in the secondary circuits such as lights and plugs. Source: https://finolex.com/all-that-you-need-to-know-about-distribution-boards/
- A distribution board or distribution panel (DP) is an important part of an electricity supply system. Its job is to split an incoming electrical power feed into multiple secondary or subsidiary circuits. Most of the time, each of these secondary circuits will be protected with a fuse or breaker. Source: https://uk.rs-online.com/web/content/discovery/ideas-and-advice/distribution-boards-guide
- Distribution boards might also be called panel-boards, breaker panels, or simply electrical panels. In the UK, distribution boards like this are often referred to as consumer units in domestic properties. The terms consumer unit and distribution board are not completely interchangeable. However, for most practical uses, they tend to mean the same thing. Source: https://uk.rs-online.com/web/content/discovery/ideas-and-advice/distribution-boards-guide
- In North America, distribution boards are generally housed in sheet metal enclosures, with the circuit breakers positioned in two columns operable from the front. Some panel-boards are provided with a door covering the breaker switch handles, but all are constructed with a dead front; that is to say the front of the enclosure (whether it has a door or not) prevents the operator of the circuit breakers from contacting live electrical parts within. Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Distribution_board
- Breakers are usually arranged in two columns. In a U.S.-style board, breaker positions are numbered left-to-right, along each row from top to bottom. This numbering system is universal across various competing manufacturers of breaker panels, so that a panel-board with a group of breakers can easily be exchanged for a different brand of panel-board, while reusing the existing branch circuit breakers. Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Distribution_board
Similar Questions
- What are electrical safety devices?
- What are electrical safety risks in the office?
- Does an Electrical Panel Need a Cover?
- What are the Requirements for Labeling Circuit Breakers?
- What Type of Labels are Used for Electrical Panels?
- How do electrical fires start and how can they be prevented?
- What are the Requirements for Electrical Panel Labeling?
- Why is Electrical Panel Labeling Important?
- How can a LOTO program improve electrical safety?

