
The hierarchy of hazards, also referred to as the hierarchy of hazard controls is an approach used to effectively address safety risks in the facility. After performing a job safety analysis, you will have a list of different kinds of hazards: chemical hazards, physical hazards, health hazards, and more. There are five levels to the hierarchy and it is often depicted as a pyramid meant to be worked from the top down.
NIOSH Hierarchy of Controls
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has designated five levels of hazard controls. These are often depicted as a pyramid meant to be worked from the top down. The five controls in the hierarchy are:
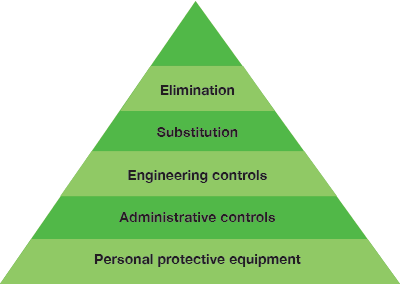 Eliminating the hazard: The most effective way to keep workers safe from a workplace hazard is to eliminate the hazard altogether. If a tool or piece of equipment represents a danger to workers and the facility you should consider the necessity of the item; if you don’t need it, get rid of it!
Eliminating the hazard: The most effective way to keep workers safe from a workplace hazard is to eliminate the hazard altogether. If a tool or piece of equipment represents a danger to workers and the facility you should consider the necessity of the item; if you don’t need it, get rid of it!- Reducing the hazard: Completely eliminating the hazard is not always a viable option, and the next strategy to consider is substituting the hazard out with something less dangerous. Even though a hazard still exists, employees will not be in nearly as much danger.
- Implementing engineering controls: After trying to eliminate or reduce the hazard, the next best option is to limit the exposure to the hazard by using engineering controls. Engineering controls are designed as modifications or designs to machines, equipment, ventilation systems, and processes that reduce the amount of exposure and physically protect the worker from harm.
- Utilizing administrative controls: Moving from the top down, the next option in the hierarchy of hazards is to use administrative controls. These types of controls are typically rules and regulations put in place to minimize risk. Posting safety signs will alert workers to risk, and implementing standards and operating procedures will ensure employees are working with or around the hazard safely.
- Personal protection equipment: Finally, at the bottom of the pyramid is personal protection equipment. Although considered “the last line of defense,” PPE can make the difference between a minor injury and a severe, life-threatening injury.
Similar Questions
- What are hazard controls?
- What is the role of PPE in workplace safety?
- What are occupational health hazards?
- What does JSA stand for?
- What is a job safety analysis?
- Why Should a Workplace Implement Hazard Controls?
- How are hazards controlled in a confined space?
- What is the difference between a job safety analysis (JSA) and a risk assessment?
- What are common safety hazards in a facility?


