
NFPA 704 is a set of standards used to identify hazardous materials so that emergency response professionals will know the dangers. While intended primarily for emergency responders, NFPA 704 is also helpful for many other people when displaying the labels, signs, and the iconic NFPA 704 Diamond.
NFPA stands for "National Fire Protection Association" and is an organization best known for creating these types of standards. This set of standards was first developed in the 1960s, but has been modified multiple times over the years to reflect the best practices.
The standards help employees and emergency responders determine what, if any, special equipment or protections should be used in the event of a spill, fire, or other emergency situation.
What Is the NFPA 704 Diamond?
The NFPA 704 Diamond is a diamond-shaped object that is split up into four sections. Each of the four sections is colored differently (blue, red, yellow, and white) and are used to indicate different types of hazards (flammability, health, instability, and special notes). Each section is typically filled in with a number between 0 and 4, which indicates the level of hazard that exists.
When this NFPA 704 diamond is used, it allows emergency responders and others to quickly evaluate the situation so they know how to react to any issues. Of course, this does require that everyone involved receives the necessary training so they can quickly see what the diamond says without having to stop and look it up.
NFPA Codes
When learning about NFPA 704, it is essential to understand all the different codes used. These codes offer specific information to those who view them and can help those in the area respond properly to minimize the danger.

NFPA 704 | Flammability (red)
The red box is found on the top of the diamond and indicates the level of danger related to flammability. Any chemicals or materials that present a flammability hazard will be assigned a number between 1 and 4 (zero indicates no significant hazard).
- 0 - The zero rating means that the material will not burn in normal fire conditions. Examples of this are stones and sand. Any material that can be exposed to a temperature of 1500 degrees for at least five minutes is rated a 0.
- 1 - Materials rated a one require a significant amount of preheating before they will ignite. Examples of this type of material include ammonia and mineral oil.
- 2 - In order to have materials rated at this level, they must be moderately heated or exposed to a high ambient temperature. This category includes things like diesel fuel.
- 3 - Any material or substance that can ignite in all common ambient temperatures as well as liquids that have a flash point below 73 degrees are in this category.
- 4 - This is the most hazardous level and includes all substances that rapidly vaporize in normal conditions. Anything with a flash point below room temperature.

NFPA 704 | Health (blue)
The blue section of the NFPA 704 diamond is located on the left side of the diamond and provides warnings about what types of health issues the material can cause.
- 0 - Materials that pose no health hazard and don't require any type of personal protective equipment are in this category.
- 1 - Any material or solution that can cause minor irritation. Examples include acetone and sodium bromate.
- 2 - Materials that can cause temporary incapacitation and/or residual injury with intense and/or continued exposure. Examples include diethyl ether and ammonium phosphate.
- 3 - Materials that can cause serious but temporary injuries or moderate residual injuries with even short exposure are rated at this level. Examples include liquid hydrogen and calcium hypochlorite.
- 4 - Anything in this category can cause very serious residual injuries or death with very short exposure. Examples include hydrofluoric acid and hydrogen cyanide.

NFPA 704 | Instability (yellow)
The yellow section of the NFPA 704 diamond is on the right side and is used to indicate hazards related to instability or reactivity.
- 0 - Any product that is normally stable in most conditions. Helium is an example of this.
- 1 - Products at this level are typically stable, but can become unstable with high temperatures or pressures. Propene is an example of this.
- 2 - If a material experiences a violent chemical change with elevated temperature or pressure, it is rated a two. Products that react violently when exposed to water are also at this level. Examples include white phosphorus, sodium, and potassium.
- 3 - Any product that can be detonated with a strong initiating source or reacts explosively with water. Examples include ammonium nitrate and chlorine trifluoride.
- 4 - Materials that are capable of detonating or exploding at normal temperatures or pressures. Examples include nitroglycerine, nitrogen triiodide, and chlorine dioxide.
NFPA 704 | Special Notes (white)
 The bottom of the NFPA 704 diamond is the white area, which is used to provide special notes or non-standard symbols. This section doesn't have the typical numbers, but instead uses symbols to identify hazards such as "OX" to indicate that the material is an oxidizer or "SA" to indicate that the product is an asphyxiate gas. There are a variety of other standard and non-standard special note symbols that can be used.
The bottom of the NFPA 704 diamond is the white area, which is used to provide special notes or non-standard symbols. This section doesn't have the typical numbers, but instead uses symbols to identify hazards such as "OX" to indicate that the material is an oxidizer or "SA" to indicate that the product is an asphyxiate gas. There are a variety of other standard and non-standard special note symbols that can be used.
Many facilities will put up an NFPA guide poster that explains all the above information in an easy-to-read format. This can be a great way to ensure the facility is always able to look up a meaning should it be necessary.
Example of a NFPA 704 Diamond
This is a graphic overview of what a standard NFPA 704 diamond looks like and what each section contains. This type of image can be printed off and posted to help people learn more about this important standard.
Importance of the NFPA Labeling System
Any facility that uses any type of hazardous material will need to have NFPA diamond labeling available. These labels can be placed directly on storage containers and shipping containers so everyone is aware of the potential risks of a particular product.
Having an industrial label printer from LabelTac® is a great way to ensure it is always possible to create new labels as they are needed. Whether a facility needs to create multiple copies of the same type of NFPA 704 diamond labels or requires lots of unique ones, these types of printers are essential.
Choosing the right type of label supply is very important since many products are stored in areas that will have special needs. If a product is stored in a moist or humid area, for example, it is necessary to have a waterproof label supply, for example. LabelTac® printers are also excellent for this type of thing because they can create bold colors that are easy to see, even from a distance.
Using NFPA Signs
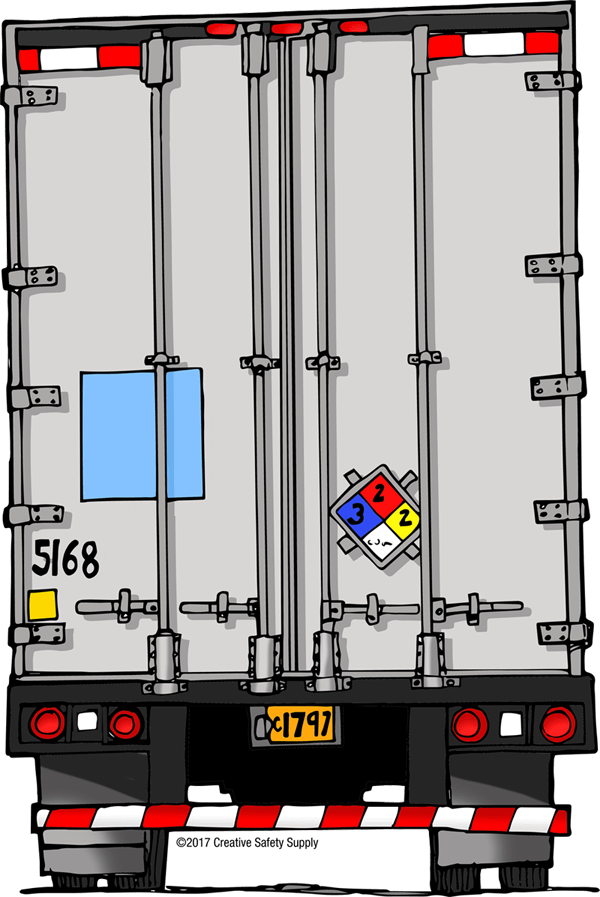
In addition to creating NFPA labels, it is often necessary to use NFPA signs, or placards. These are often made of metal or plastic and are attached to trucks and other vehicles that transport hazardous materials.
Having the NFPA signs on a vehicle is an important safety precaution for many reasons. If an emergency responder sees this sign on a vehicle that was in an accident, they will be able to quickly take the proper precautions based on what type of hazardous materials are being transported. These signs can also help streamline the inspection process, should that be necessary.
NFPA Signs with Additional Information
In addition to signs that display only the NFPA diamond, it is also common to have a sign that has the diamond as well as other warnings. This helps ensure that people in the area understand the danger even if they are not familiar with all the NFPA 704 codes. The following image is an excellent example. It alerts people to the danger, lists what the hazardous product is (propane) and gives instructions for what type of activities to avoid.
Adjustable NFPA Diamond Signs
For vehicles that transport many types of chemicals or other hazardous materials, using an adjustable NFPA sign is an ideal solution. When a truck is being loaded, the sign can be adjusted to display the proper information based on what is being transported at that time. Once the right numbers or symbols are shown in each section of the diamond, the sign is locked down and ready for transport.
Implementing NFPA 704 Standards
While the NFPA 704 standards are entirely voluntary, most companies that deal with hazardous materials agree that it is a good idea to use them. When implementing this type of standard in a facility, it is important to take the time to ensure it is done properly. This means providing training to employees and others in the facility and ensuring all the right signs, labels, and other resources are available right from the beginning.
Sources
- https://www.nfpa.org/codes-and-standards/all-codes-and-standards/list-of-codes-and-standards?mode=code&code=704
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Fire_Protection_Association
Similar Articles
- Understanding the NFPA 704 Diamond Labeling System
- Medical Substance Pipe Marking | NFPA99/CGA C-9
- NFPA 855: The Installation of Stationary Energy Storage Systems
- NFPA 70E [Workplace Electrical Safety]
- NFPA 25: Standards for Fire Protection Systems
- Hazardous Materials Identification System (HMIS Labels)
- NFPA 99: Understanding the Health Care Facilities Code
- Anhydrous Ammonia – Safety & Labeling
- ANSI Z535 [Updated Guide to Safety Signs & Labels]
- Arc Flash PPE


