
CCP stands for Critical Control Point, a point at which preventative measures must be applied in order to reduce, prevent, or eliminate a safety hazard. Most widely used in the food industry, CCPs are essential steps within a business’s entire process, from purchasing raw ingredients right through to preparation. Hazards that may put a risk to food safety include chemical contamination and bacterial growth. CCPs to mitigate these hazards include testing ingredients for metal contaminants or chemical residues, and properly storing chicken and other types of meat that will develop bacteria when left at room temperature.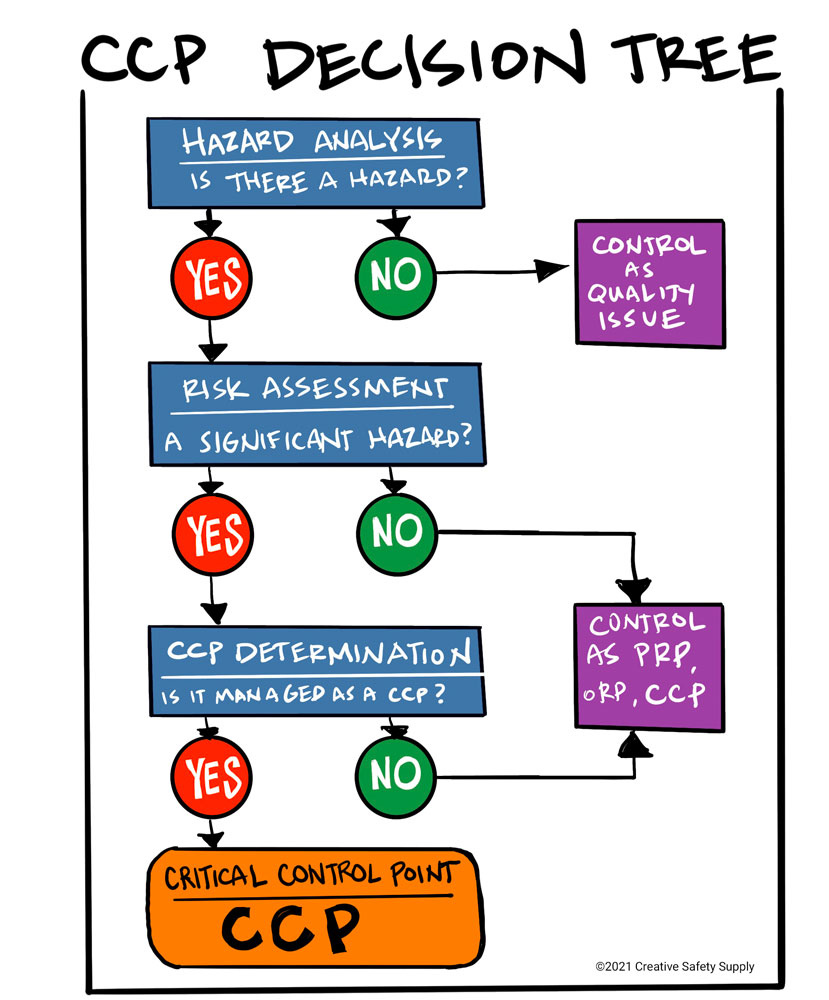
To identify Critical Control Points in your business’s process, a hazard analysis must first be conducted to determine all the food safety hazards that may reasonably occur. After the analysis, controls are established in order to address the known risks. Together, an analysis and control points are known as HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points), a preventative approach to food safety and the basis for many food safety programs around the world.
The CCP Decision Tree
A strategy that can be used to help identify CCPs is a decision tree. CCP decision trees help visualize and identify each step of the process, whether a safety hazard may occur at that step, and whether a task can be performed to prevent, reduce, or eliminate the hazard.
If the task is vital for food safety, it is a Critical Control Point. Decision trees may also help determine whether the hazard can be completely eliminated, or if can only be reduced to an acceptable level. Once the hazards and CCPs have been identified, control measures will be established.
An important consideration for each CCP in your business is to assign employees responsible for monitoring procedures. If a process or product does not meet critical limits, this should be reported immediately and a plan should be put in place. CCPs should also be developed and documented carefully; this paperwork may later on prove that foods were indeed produced safely. Having Critical Control Points implemented as part of a food safety program helps to protect the health and safety of customers, and prevents businesses from suffering the consequences of serving contaminated food.
Additional CCP facts:
- CCP stands for Critical Control Point, which is a point, step or procedure in a food production process where control measures can be applied to prevent, reduce or eliminate a food safety hazard. Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Critical_control_point
- CCP is one of the key principles of HACCP, which is a systematic approach to the identification, prevention and control of food safety hazards from harvest to consumption. Source: https://www.fda.gov/food/hazard-analysis-critical-control-point-haccp/haccp-principles-application-guidelines
- CCP can be determined by conducting a hazard analysis, which involves identifying the potential hazards in each step of the food production process, assessing the likelihood and severity of the hazards, and deciding which ones need to be controlled. Source: https://www.fsis.usda.gov/sites/default/files/media_file/2021-02/16_IM_HACCP_Principles.pdf
- CCP must have critical limits, which are the maximum or minimum values to which a physical, biological or chemical hazard must be controlled at a CCP to prevent, eliminate or reduce it to an acceptable level. Source: https://www.safeopedia.com/definition/9316/critical-control-point-ccp
- CCP must also have monitoring procedures, which are the planned sequence of observations or measurements to assess whether a CCP is under control and to produce an accurate record for future use in verification. Source: https://blog.foodsafety.com.au/what-critical-control-point
- CCP can vary depending on the type of food, the processing method, the equipment used, and the intended use and consumers of the food. Source: https://www.fooddocs.com/post/critical-control-points
Similar Questions
- What does HACCP stand for?
- What does JSA stand for?
- What is composite risk management (CRM)?
- What is a job safety analysis?
- What is the difference between a job safety analysis (JSA) and a risk assessment?
- What is the hierarchy of hazards?
- What is EHS?
- What does CDC stand for?
- What is the role of PPE in workplace safety?


